94
available is via the offshore terminal in the Gulf. Between 90-95% of southern Iraq’s production passes through the
export terminal at Fao.
In 2012, Iraq exported 2.4 million bbl/d of crude oil, according to tanker data from Lloyd’s List Intelligence. The
majority of Iraqi oil exports go to the United States and to refineries in Asia, particularly India, China and South Korea.
Gas
According to the BP Statistical Review, Iraq had 3.6 Tcm of proven natural gas reserves as at 31 December 2013 with
the majority of the reserves are held as associated gas from the southern fields. According to the BP Statistical Review,
in 2013, Iraqi natural gas production was 0.6 Bcm.
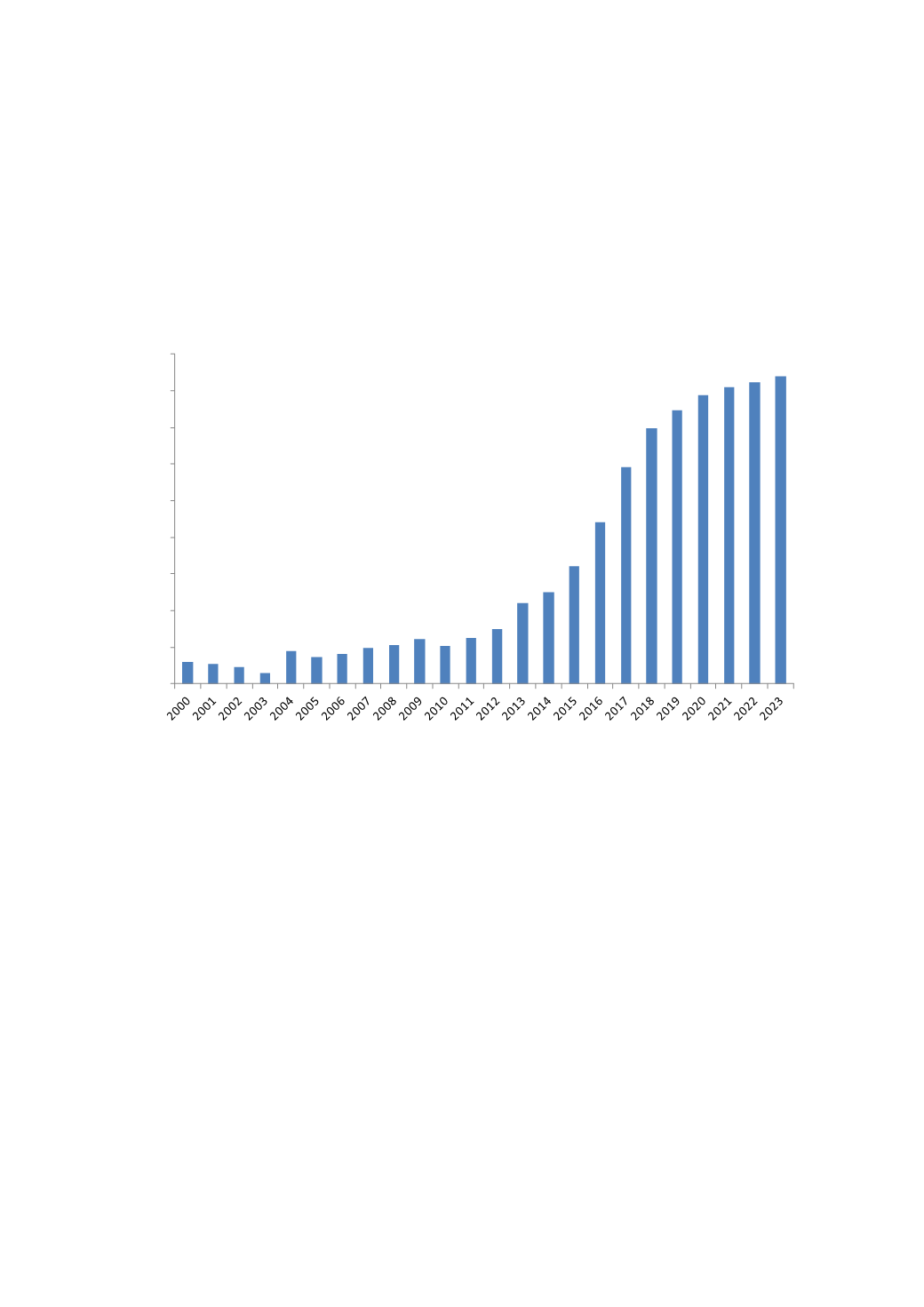
Iraq Gas Production 2000-2023
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
3,000
3,500
4,000
4,500
mmcfd
Source: Wood Mackenzie (April 2014), BP Statistical Review of World Energy (June 2014).
Some of this natural gas is used as fuel for power generation, while a portion of it is reinjected to enhance oil recovery.
However, the majority of Iraqi natural gas production is flared. Flaring losses in some months have exceeded 60% of
production due to a lack of sufficient pipelines and other infrastructure to transport it for consumption and export. To
reduce flaring, Iraq signed an agreement with Royal Dutch Shell to create a new joint venture, Basrah Gas Company, to
capture flared gas in the Basrah Province. Plans to export natural gas remain controversial because natural gas is needed
as a feedstock for Iraq’s electric power plants. Although gas development in the next five years will be focused on the
expansion of gas-fired power generation, in the longer term a number of gas export routes are feasible e.g. Syria, Kuwait,
Turkey, Jordan and Saudi Arabia are gas short, but supplying gas to these markets will require complex negotiations.
Yemen
Yemen is a small non-OPEC oil producer, facing continued decline in output. Due to the materiality of discoveries in the
country, production in Yemen has historically been dominated by small to medium sized international companies.
Despite ongoing security concerns, attractive fiscal terms and relatively low capital expenditure and operating costs per
barrel mean that attractive returns on investments can be made in Yemen for operators prepared to accept the risks.
Oil
According to the BP Statistical Review, Yemen had total proven oil reserves of approximately 3 billion barrels as at 31
December 2013, with no change from 31 December 2012. According to the BP Statistical Review, Yemen’s total oil
production in 2013 averaged approximately 161,000 bbl/d, down from 180,000 bbl/d as at 31 December 2012.
Production has been declining steadily since reaching a peak in 2002 at 460,000 bbl/d, due to a lack of sufficient new
investment in exploration and inadequate maintenance of facilities. The majority of Yemen’s production comes from six
main geographical areas: Jannah and Iyad in central Yemen, Marib and Jawf in the north and Shabwa and Masila in the


